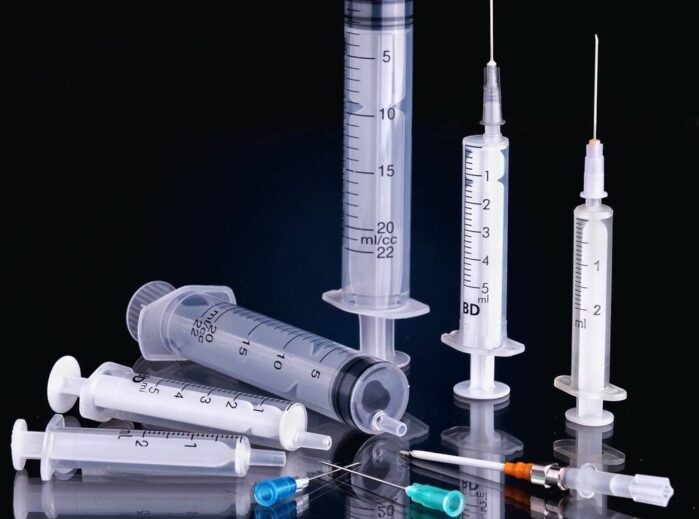
Medical syringes are an essential tool used in healthcare for administering medications and vaccines to patients. They come in various sizes and types, and are made using a specific production process. In this article, we will discuss the species, types, production process, distribution of industry chain, manufacture plant quantity, and capacity of medical syringes.
Species
Medical syringes can be classified into two species: disposable and reusable syringes. Disposable syringes are designed for single use and are made from plastic or glass. They are typically pre-filled with medication and come with a needle attached or can be attached separately. Reusable syringes, on the other hand, are designed for multiple use and are made from glass or stainless steel. They are sterilized after each use and can be used with interchangeable needles.
Types
Medical syringes come in different types, including Luer-Lock syringes, insulin syringes, safety syringes, and prefilled syringes. Luer-Lock syringes have a twist-lock mechanism that securely attaches the needle to the syringe. Insulin syringes are specifically designed for the injection of insulin and are marked with a scale that measures the dose in units. Safety syringes have features that reduce the risk of needlestick injuries, such as a retractable needle. Prefilled syringes are pre-filled with medication and are used to deliver precise doses of medication.
Production Process
The production process of medical syringes typically involves several steps, including the manufacturing of the barrel, plunger, and needle. The barrel and plunger are made using injection molding, a process where molten plastic is injected into a mold and cooled to form the desired shape. The needle is made using a process called cannula manufacturing, where a thin metal tube is drawn through a series of dies to form the shape of the needle.
Once the components are manufactured, they are assembled into the final product. The needle is attached to the barrel and plunger, and the syringe is sterilized using ethylene oxide gas or gamma irradiation.
Distribution of Industry Chain
The medical syringe industry chain is composed of several stages, including raw material production, component manufacturing, syringe assembly, and distribution. Raw materials, such as plastic and glass, are produced by suppliers and sold to component manufacturers. Component manufacturers produce the barrel, plunger, and needle and sell them to syringe assembly plants. Syringe assembly plants assemble the components into the final product and distribute them to hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare providers.
Manufacture Plant Quantity and Capacity
The manufacture plant quantity and capacity of medical syringes vary depending on the company and location. Many of the largest medical syringe manufacturers are based in Asia, particularly in China and India. According to a recent report by Allied Market Research, the global medical syringe market was valued at $5.7 billion in 2020, with Asia-Pacific accounting for the largest share of the market. The report also projects that the market will continue to grow in the coming years, driven by increasing demand for vaccines and the growing prevalence of chronic diseases.
In conclusion, medical syringes are an essential tool in healthcare, used for administering medications and vaccines to patients. They come in various sizes and types and are made using a specific production process. The medical syringe industry chain is composed of several stages, including raw material production, component manufacturing, syringe assembly, and distribution. The manufacture plant quantity and capacity of medical syringes vary depending on the company and location, with many of the largest manufacturers based in Asia.